The International Monetary Fund (IMF) confirmed that Greece had not made its scheduled 1.6 billion euro loan repayment to the fund. As a result the IMF will report that Greece is in arrears – the official euphemism for default.
Consequently Greece runs the risk to of losing access to a 1.8 billion euro loan tranche and 10.0 billion euro’s for recapitalizing banks.
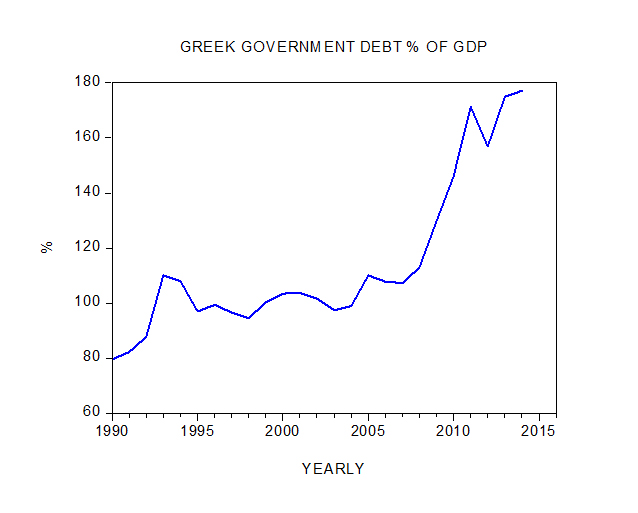
Commentators are of the view that the key factor behind the troubles in Greece is high government debt, which as a percentage of GDP stood at over 177% in 2014 against 79.6% in 1990.
We suggest that it is not debt as such that is behind the current crisis in Greece but instead large government outlays and strong increases in the money supply.
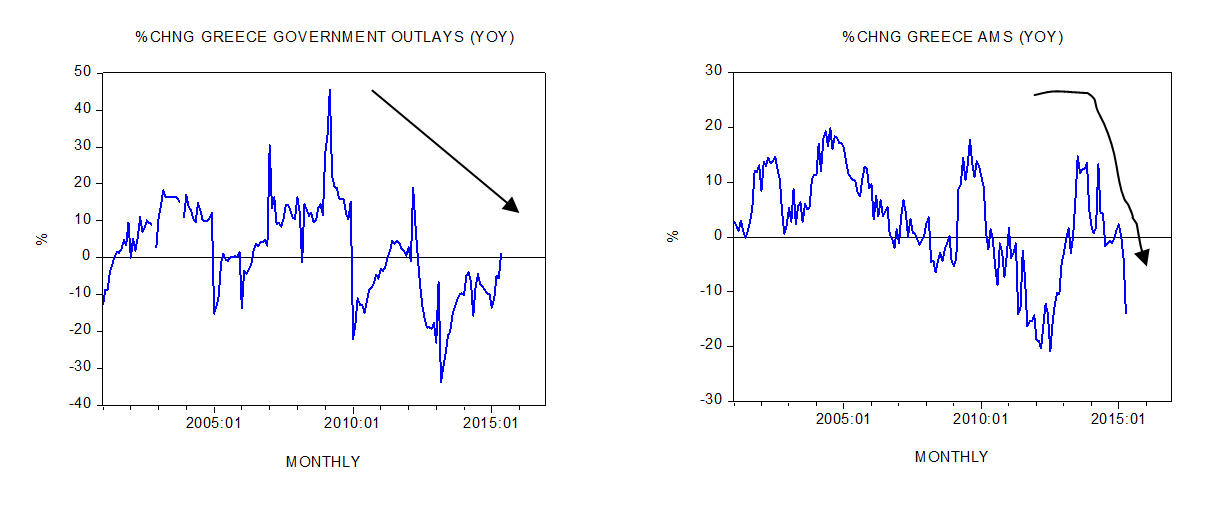
Since early 2000 the underlying trend in the growth momentum of government outlays was heading up with the yearly rate of growth closing at 45.5% in March 2009. Since then the trend in the growth momentum has been declining.
Year on year the rate of growth of Greece’s monetary measure AMS stood at 20% in July 2004. It stood at a lofty 18% in August 2009 before sliding to minus 13.8% in April this year.
Loose fiscal and monetary policies have been instrumental in the generation of various non-productive activities that have been squandering wealth.
A fall in the growth momentum of both government outlays and the money supply weakens the destruction of the wealth generation process.
A decline in the growth momentum of government outlays and money supply (see charts) has arrested the diversion of wealth to non-productive activities from wealth generating activities.
We suggest that the current crisis is centered around non-productive activities that can no longer divert wealth from wealth generating activities on account of a fall in both government spending and the money supply rate of growth.
From this perspective this is good news for the Greek economy. (Hence what is needed is to maintain a tight grip on government outlays and allow the plunge in the money supply to continue).
We hold that Greece’s wealth generating process has been badly damaged as a result of past loose fiscal and monetary policies, hence reverting back to loose fiscal and monetary policies as suggested by various famous economists such as a Nobel Prize Laureate in economics Joseph Stiglitz is going to make things much worse.
Remember, neither more government outlays and more monetary pumping can generate real wealth – only the strengthening of the wealth generating private sector can do that.
Now, since currently non-productive activities are likely to comprise a large portion of total activities, the effect that is generated from their demise appears to be very severe.
After closing at 122 in April 2008 industrial production index plunged to 91 by March this year – a fall of 25.3%. The unemployment rate climbed from 7.3% in May 2008 to 25.6% in March this year.
We maintain that any threat to the financial systems of other European economies is not due to the Greek default, but instead is a result of loose fiscal and monetary policies that have damaged the savings bases of various European countries.
Rather than continuing to support wealth squandering activities and thereby making things much worse, a better way is to allow wealth generators to step in and let them restart the wealth generating process. This means that all the loopholes of money creation should be sealed and government outlays should be cut to the bone. Obviously such measures will be painful for various individuals employed in non-wealth generating activities. Failing to reduce non-productive activities however will only prolong the agony – it is not possible to create real wealth out of nothing.
Conclusions
We suggest that key factors behind Greece’s economic crisis are past loose fiscal and monetary policies. We also hold that the current crisis is centred around non-productive activities that can no longer divert wealth from wealth generating activities on account of a fall the yearly rate of growth in both government outlays and the money supply.